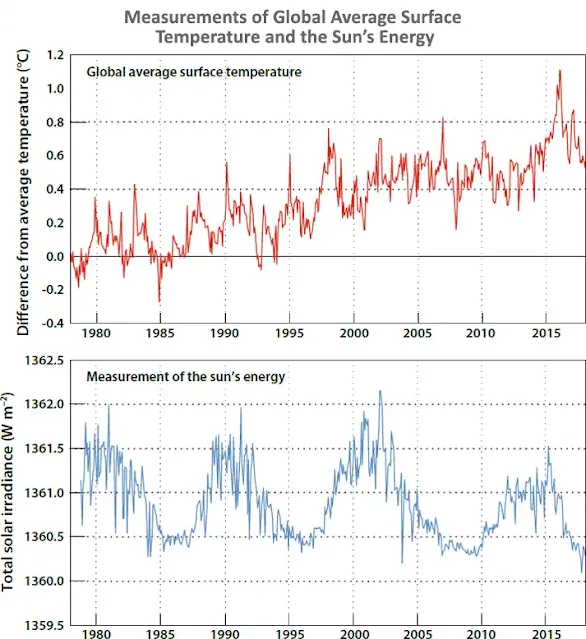
Climate change has emerged as a pervasive and urgent issue in today's world, affecting ecosystems, weather patterns, and human societies. Comprehending the causes of climate change is pivotal for formulating effective solutions to alleviate its impacts. In this article, we explore the intricate web of factors contributing to climate change, shedding light on both natural and anthropogenic elements.
Causes of Climate Change
Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Cause of Climate Change
At the forefront of climate change causes lies the substantial increase in greenhouse gas emissions. Human activities, especially the combustion of fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas, release vast amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere. These gases trap heat, creating a greenhouse effect that warms the Earth's surface. Additionally, other greenhouse gases like methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O) contribute to the problem, intensifying the heat-trapping effect.
To combat the causes of climate change, there is a pressing need to transition towards sustainable and renewable energy sources, reducing our dependence on fossil fuels.
Deforestation: Major Cause of Climate Change
The destruction of forests is a significant contributor to climate change. Trees act as carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 during photosynthesis and storing carbon in their biomass. However, widespread deforestation diminishes this vital carbon-absorbing capacity, releasing stored carbon into the atmosphere. Moreover, the loss of trees means less oxygen production and disruption of ecosystems, exacerbating the environmental impact.
Efforts to combat climate change must include initiatives to curb deforestation, promote reforestation, and adopt sustainable land-use practices.
Industrial Activities:
Industrial processes, including manufacturing, substantially contribute to climate change through the release of greenhouse gases and other pollutants. Factories emit large amounts of CO2, methane, and nitrous oxide during production and energy generation. Furthermore, certain industries release potent synthetic greenhouse gases, such as hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), which have a significantly higher warming potential than CO2.
Adopting cleaner technologies, enhancing energy efficiency, and implementing stringent emission control measures are vital steps in mitigating the impact of industrial activities on climate change.
Agriculture:
Agricultural practices also play a role in climate change, primarily through the release of methane and nitrous oxide. Livestock, particularly cattle, produce methane during digestion, and the use of nitrogen-based fertilizers contributes to nitrous oxide emissions. Additionally, agricultural expansion often leads to deforestation, compounding the environmental impact.
Sustainable farming practices, improved livestock management, and the promotion of agroecology can help minimize the agricultural sector's contribution to climate change.
Transportation:
The global transportation sector is a significant source of greenhouse gas emissions, primarily from the combustion of fossil fuels in vehicles. Cars, trucks, airplanes, and ships collectively contribute to the rising levels of CO2 in the atmosphere. Transitioning to electric vehicles, improving fuel efficiency, and investing in public transportation are essential strategies to reduce the carbon footprint of the transportation sector.
Urbanization:
Rapid urbanization contributes to climate change through increased energy consumption, altered land-use patterns, and the heat island effect. Urban areas often experience higher temperatures than surrounding rural areas due to the abundance of concrete and asphalt, which absorb and retain heat. This phenomenon exacerbates the overall warming of the planet.
Green urban planning, the development of sustainable infrastructure, and the incorporation of green spaces within cities are critical components of climate change mitigation in urban settings.
Land Use Changes:
Alterations in land use, including urban expansion, agricultural intensification, and deforestation, contribute to changes in the Earth's surface properties. These changes can influence local and regional climates, impacting temperature, precipitation patterns, and atmospheric circulation. The interconnectedness of land use changes with climate change highlights the need for holistic approaches in addressing these issues.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, climate change is a multifaceted challenge with roots in both natural processes and human activities. By understanding the causes, we can develop effective strategies to mitigate its impact and work towards a sustainable future. A comprehensive approach that addresses the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, sustainable land-use practices, and the promotion of clean energy technologies is imperative. Only through collective efforts and a commitment to environmental stewardship can we hope to address the causes of climate change and safeguard the planet for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Climate Change:
Q1: What are the 5 main causes of climate change?
A1: The five primary causes of climate change are:
Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Burning fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O), triggering a greenhouse effect that traps heat in the Earth's atmosphere.
Deforestation: The destruction of forests diminishes the planet's capacity to absorb carbon dioxide, leading to increased atmospheric CO2 levels.
Industrial Activities: Manufacturing processes and energy production release substantial amounts of greenhouse gases and pollutants into the atmosphere, intensifying the greenhouse effect.
Agriculture: Livestock farming and the use of nitrogen-based fertilizers contribute to methane and nitrous oxide emissions, respectively.
Transportation: The combustion of fossil fuels in vehicles, airplanes, and ships releases CO2, contributing to the overall rise in greenhouse gas concentrations.
Q2: What are the 3 main changes caused by climate change?
A2: The three principal changes induced by climate change are:
Rising Temperatures: Global temperatures are on the rise, resulting in heatwaves, altered weather patterns, and ecosystem changes.
Sea Level Rise: Melting ice caps and glaciers, coupled with the thermal expansion of seawater, lead to rising sea levels, affecting coastal regions and low-lying areas.
Extreme Weather Events: Climate change is associated with an escalation in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, encompassing hurricanes, floods, droughts, and wildfires.
Q3: What is the cause of climate change?
A3: The primary cause of climate change is the heightened concentration of greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere. Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, industrial processes, and specific agricultural practices, release these gases, creating a greenhouse effect that traps heat and results in global warming.
Q4: What causes climate change for dummies?
A4: Climate change, in simple terms, is caused by the accumulation of certain gases in the air, commonly referred to as greenhouse gases. Gases like carbon dioxide and methane trap heat from the sun in the Earth's atmosphere, leading to a warming effect. Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and specific farming practices, release substantial amounts of these gases, intensifying the natural greenhouse effect. Consequently, the planet's climate is changing, causing shifts in temperature, weather patterns, and sea levels.