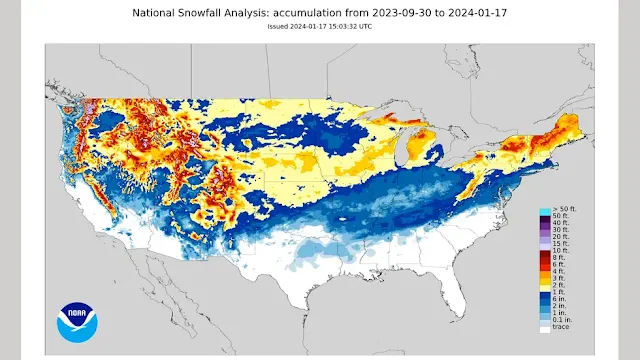
As we enter the peak of the western U.S. water season, now is an opportune moment to assess potential water resources for the upcoming summer. Initially, concerns loomed about the prospect of an El Nino winter bringing either drought or flooding. Fortunately, it seems those worries were unfounded.
Let's delve into the crucial details, commencing with California's reservoir levels – a source of significant concern just two years ago. The good news is, as indicated below, California's reservoirs are not only in good shape but generally above normal levels. Key reservoirs such as Shasta and Oroville boast levels at 121% and 131% of normal, respectively, with others also maintaining robust levels.
Heading north, the water levels behind the Grand Coulee Dam in Washington State surpass normal levels, promising benefits for both power generation and fish.
Now, what about Seattle's reservoir levels? In December, they plummeted well below normal, causing concern. However, as of January 22 (see below), recent rains have elevated them to nearly normal levels. With more substantial rains anticipated and a near-normal snowpack in relevant mountain areas, Seattle seems well-positioned waterwise for the summer.
Moving on to the current snowpack in the Northwest, Oregon's average sits slightly above 100%, indicating a positive situation. Washington, while slightly below normal overall, shows improvement in critical Cascade watersheds at around 80%, up from a month ago. The Yakima drainage stands at a promising 91%.
Looking ahead, the West Coast can expect a wet week. The Pacific Northwest and British Columbia will experience moderate atmospheric rivers, followed by a significant four-day total of precipitation moving down into California from southern Oregon to Baja California.
In summary, the water situation for most of the West Coast appears relatively favorable. However, it's essential to monitor specific areas, such as the Yakima River storage, currently at 60% of normal. With a 91% snowpack and ample precipitation anticipated, optimism remains that conditions will improve.
Lastly, as El Nino rapidly weakens, its impacts are expected to fade in the upcoming months, further contributing to the positive outlook for West Coast water resources.